Oracle Financial Services Cloud
Modernizing Mid-Market Retail Banking with Oracle's Cloud-Based, API-Driven Solution
Product Design | Digital Transformation
Note: This is a broad, high-level summary of the product, intentionally kept general to ensure compliance with my Non-Disclosure Agreement

About the project
Oracle Financial Services Cloud is a cloud-native, multi-tenant platform designed to serve financial institutions, with an initial focus on US Mid-Market Retail Banking. It follows a Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) model and is built using microservices architecture, allowing flexibility, scalability, and rapid deployment of new services.
Business Goal
Oracle aims to modernize and digitize mid-market retail banking by offering a cloud-based, API-driven, and highly configurable solution. The focus is on enhancing operational efficiency, accelerating service innovation, and improving developer experience while ensuring scalability and security for financial institutions.
Cloud Services Offered
The platform offers a comprehensive suite of financial cloud services designed to streamline banking operations, enhance customer interactions, and integrate third-party financial solutions. These services include:
-
Communication Cloud Service – This service facilitates seamless communication between financial institutions and their customers. It likely supports messaging, notifications, and alerts across various channels such as email, SMS, and in-app messaging. It ensures timely updates regarding account activities, transaction confirmations, and regulatory communications, enhancing customer engagement and compliance.
-
Deposit Origination Cloud Service – This service simplifies the process of opening and managing deposit accounts. It provides financial institutions with tools to onboard customers efficiently, verify applicant details, configure account plans, and define eligibility criteria. It plays a crucial role in streamlining customer acquisition and automating workflows related to new account creation.
-
Deposit Servicing Cloud Service – Designed to handle the ongoing management of deposit accounts, this service ensures smooth operations post-account creation. It includes functionalities for interest calculations, fund movements, transaction tracking, and currency management. It also supports scheduling mechanisms for financial events, such as interest payouts and scheduled debits, to ensure efficient account servicing.
-
Financial Services Marketplace Cloud Service – This service acts as an integration hub for financial institutions, allowing them to connect with third-party financial service providers. It facilitates seamless collaboration between banks and fintech companies, enabling them to offer a wide range of financial products and services. It also supports supplier management, product configurations, and multi-tenant banking models, creating an ecosystem where financial services can be customized and scaled.
Problem Statement
Financial institutions face challenges in adopting cloud-based solutions due to complex onboarding, fragmented workflows, and lack of customization. Additionally, users—bank administrators, IT teams, and financial officers—struggle with understanding microservices integration, navigating multiple cloud services, and configuring workflows effectively.
Due to my NDA, I can only provide an overview of the research and cannot share detailed insights into the user research conducted.
User Research & Key Insights
Primary User Groups:
-
Bank Administrators – Responsible for configuring financial services and managing security.
-
IT Teams – Handle integration, API management, and system maintenance.
-
Financial Officers – Oversee transactions, account services, and compliance.
Research Methodology:
-
User Interviews with 10+ banking professionals
-
Competitor Analysis of cloud-based financial solutions
Key Findings:
-
High Learning Curve: Users found it difficult to understand microservices-based workflows.
-
Fragmented Navigation: Switching between different cloud services was cumbersome.
-
Configuration Overload: Bank admins struggled with setting up financial services due to overwhelming options.
UX Design Solutions
1. Intuitive Onboarding & Guided Workflows
-
Design an interactive wizard-based onboarding process to guide users through initial setup.
-
Implement app tooltips and contextual help sections for complex configurations.
2. Unified Dashboard for Seamless Navigation
-
Create a centralized dashboard with a service overview panel to access multiple cloud services (e.g., Deposit Origination, Communication Cloud, etc.) in one place.
-
Create an intuitive design with a well-structured information hierarchy and integrate a universal search feature.
3. Simplified Configuration with Pre-Built Templates
-
Develop a pre-configured templates for common banking workflows, while reducing setup time.
-
Enable a drag-and-drop interface for custom configurations.
4. Enhanced API Documentation & Developer Tools
-
Introduce an API sandbox environment for testing integrations before deployment.
-
Provide step-by-step API guides and auto-generated code snippets for ease of use.
To streamline navigation across various cloud services and enhance workflow configuration, we integrated all four services into a unified, centralized dashboard within the Oracle Financial Services Cloud (OFSC) product. By consolidating these services, we introduced a service overview panel, allowing users to seamlessly access and interact with multiple cloud services in a single interface.
Improving the information hierarchy and ensuring that each service is clearly categorized and accessible through distinct domains. We are making an intuitive user experience that simplifies the management of complex cloud operations. Below is an illustration of the OFSC dashboard.

As a Senior UX Designer, my responsibilities encompass overseeing the entire end-to-end design process for various domains within the Deposit Origination Cloud Service (DOCS). I take ownership of the user experience design and documentation across these domains, ensuring that each component aligns with the product's goals and user needs. One of the key domains I have worked on is the Beneficiary Domain. Below is a detailed explanation of my work and contributions to this specific domain, outlining the overall process of working on an individual domain.
My Role & Contribution
Beneficiary Domain UX Process
Kickoff
Beneficiary Domain
Whenever we start working on an individual domain, the first step before diving into the actual work is to hold a kickoff meeting with the product managers. During this session, the product manager would provide an overview of the domain, covering key aspects such as:
-
What is a Beneficiary? Understanding its definition, purpose, and role within the system.
-
Why is it needed? Exploring its significance, the problems it solves, and its impact on users or business processes.
-
How is it configured in our product, OFSC? Gaining insights into how the Beneficiary concept is structured, implemented, and integrated within Oracle Field Service Cloud (OFSC).
This meeting would help establish a clear understanding of the domain, align expectations, and ensure that all team members have the necessary context before moving forward with design and development work.





Data Model
Data Model and Data Dictionary
After that, we are provided with a data model, which serves as the foundation for structuring and organizing the information. This model defines the relationships between different data entities, specifying attributes, constraints, and how they interact within the system. It plays a crucial role in ensuring data consistency, integrity, and usability across the application.


User Goal
Defining User, Goal and Motivation
After receiving the data model and data dictionary, we proceed to define the key aspects of the problem we are addressing. This involves identifying the target users—who they are, their roles, and their specific needs. We then clarify the precise objectives we aim to achieve, ensuring alignment with user requirements and business goals. Additionally, we analyze the underlying reasons behind these objectives, understanding why accomplishing this goal is essential for the users. In essence, this step is about defining the user goal, which serves as the foundation for our solution approach.


Scope of Work
Scope of Work: Defining Configuration Services and Information Architecture
Once our user goal is defined we then move to our next section which is defining the scope of work, where we begin by determining the Configuration (CRUD) services for the Beneficiary module. CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) operations form the foundation of data management, enabling users to interact with and modify beneficiary-related information. These services ensure that the system can efficiently handle data entry, retrieval, modifications, and removals while maintaining data integrity and security.
Once the CRUD services are established, we proceed to define a high-level information architecture. This involves structuring and organizing data, workflows, and user interactions within the system to ensure seamless navigation and efficient data accessibility. The information architecture serves as a blueprint for how different components of the system interconnect, outlining:
-
Data Flow – How information moves between different modules.
-
User Access and Permissions – Who can view, modify, or delete data.
-
System Interactions – How external or internal services integrate.
-
Hierarchy and Categorization – Logical grouping of data and functionalities.
This step is crucial for ensuring a well-structured and scalable system that aligns with business goals and user requirements.

Next Steps: Advancing UX Design and Implementation
As we move forward, the next steps involve identifying the appropriate Redwood components and design patterns that can be leveraged to ensure consistency, efficiency, and alignment with Oracle’s design system. This includes:
-
Identify Redwood Components & Patterns – Review existing Redwood UI components and patterns to ensure consistency and efficiency. Determine if new components are needed.
-
Create or Modify UX Patterns – Develop new UX patterns if required or refine existing ones to align with user needs and Redwood guidelines.
-
Design High-Fidelity Wireframes & Prototypes – Build detailed wireframes and interactive prototypes to validate user flows and interactions.
-
Explore Desktop Redwood Design – Optimize Redwood design for desktop interfaces, ensuring responsiveness, usability, and seamless cross-device consistency.
Establishing Consistent UX Patterns Before Wireframing
Before diving into wireframing, we ensure that our design patterns for record creation are already well-defined. This approach maintains consistency across the product and streamlines the design process.
To achieve this, before even beginning domain-specific designs, we brainstormed and explored various potential flows and patterns. Through iterative experimentation and refinement, we carefully evaluated multiple approaches. After thorough consideration, we finalized a standardized pattern and documented it for future reference.
Now, whenever we start designing a new domain, we refer to this documented pattern to ensure consistency. If we encounter a new requirement that isn’t covered in the existing documentation, the entire team collaborates to brainstorm potential solutions. After evaluating different approaches, the most effective pattern is implemented and formally added to the documentation.
This structured approach ensures that our product remains cohesive, scalable, and user-friendly, while also allowing for adaptability when new challenges arise.
For demonstration purposes, here are a few screens showcasing how we documented our patterns in Figma



For demonstration purposes, this video showcases an overview of UX documentation on a Confluence page, which developers and other team members refer to

Understanding the Beneficiary Feature in Oracle Field Service Cloud (OFSC)
In the Oracle Field Service Cloud (OFSC) application, the Beneficiary is a designated feature that allows users to manage relevant settings and configurations. To access this feature, navigate to Configuration > Beneficiary within the application. This section provides tools and options for defining, managing, and customizing beneficiary-related parameters to align with organizational needs.

Please check these links for a more detailed inspection: Figma File Link and Prototype Link



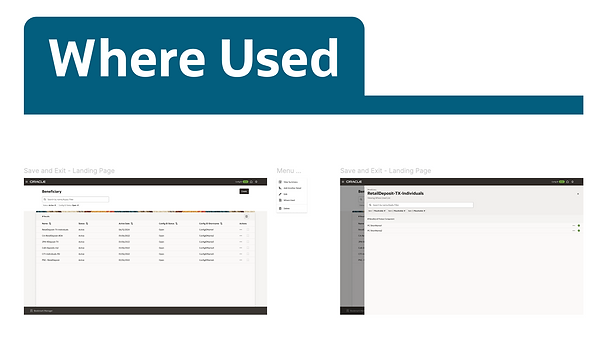



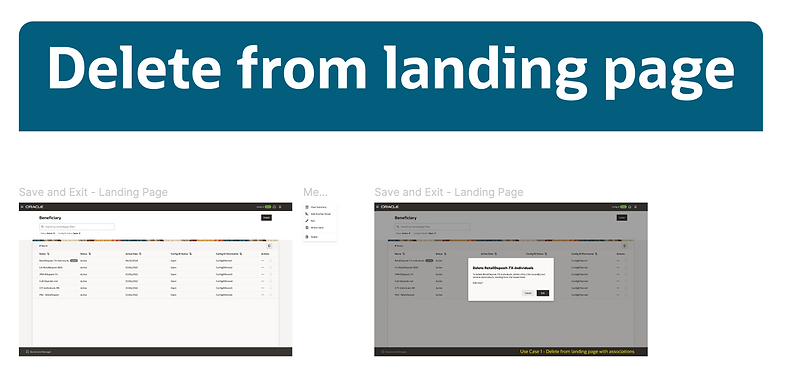


Handoff
Once we complete the domain wireframes, we conduct a detailed walkthrough of the user flow with the product managers and engineering team. This ensures that everyone is aligned on the proposed design and that the flow is feasible for implementation using our existing Redwood components.
After incorporating any necessary feedback and finalizing the design, we officially hand it off by documenting all relevant links on the Confluence page. This includes sections such as Initiation, Discovery, Design, and Handoff along with any supporting materials required for a smooth development process.
Finally, we close the associated Jira tickets to mark the completion of our design phase. Below is the overview video and the corresponding Confluence handoff page.

Challenges
Designing for the Beneficiary domain in Oracle Field Service Cloud (OFSC) required addressing multiple complexities to create a user-friendly and efficient experience. This process involved:
-
Handling Complex Business Rules: The beneficiary domain operates within a framework of intricate rules, requiring careful design to ensure compliance, accuracy, and logical flow in user interactions.
-
Adapting Screens for Diverse Scenarios: Since beneficiaries may have varying attributes, statuses, and configurations, the interface needed to be flexible enough to accommodate different use cases while maintaining consistency.
-
Simplifying Intricate Terminology: Beneficiary-related terminology can be complex and industry-specific. The design had to present this information in a clear and intuitive manner, ensuring that users could quickly understand and act upon it.
-
Ensuring Seamless User Flows: Given the predefined design patterns in OFSC, maintaining a smooth user journey was crucial. This involved structuring the interface to reduce cognitive load, optimize task completion, and minimize errors.
-
Working Within Strict Design Patterns: The OFSC platform has established UI/UX guidelines, limiting the ability to create entirely new design solutions. The challenge was to innovate within these constraints, enhancing usability without deviating from existing frameworks.
By addressing these challenges, the Beneficiary feature was designed to be intuitive, scalable, and aligned with OFSC’s broader ecosystem, enabling users to manage beneficiary-related configurations efficiently.